Many businesses operate with seasonal peaks and valleys. Retail stores flourish in their busy holiday season. Construction contractors are busy when the weather is good. Accountants are very busy from January through April, but also experience a quarterly peak in July and October.

Your business many have its own calendar of busy and slow times. If your business goes through slow times, then your cash flow may suffer at certain times of the year. But having seasonal sales is only one of the reasons for a bumpy cash flow.
You might also have a business where annual payments are made for many items such as equipment purchases, software licenses, insurance renewals, and other large costs. On the revenue side, it could be that your clients pay you annually, which can be hard to predict.
There are many solutions that can help to smooth out the seasonal bumps, and here are a few ideas for your consideration.
Plan for Prosperity
 When income and expenses go up and down and up and down, it’s really hard to know if you have enough money for obligations coming up. Creating a budget can help a great deal. Consider creating two budgets: one that shows the ups and downs and one that averages a year’s income and expenses into twelve equal parts.
When income and expenses go up and down and up and down, it’s really hard to know if you have enough money for obligations coming up. Creating a budget can help a great deal. Consider creating two budgets: one that shows the ups and downs and one that averages a year’s income and expenses into twelve equal parts.
With both budgets, you’ll be able to see which months will be deviating from average and by how much. From there, it’s easy to create some forecasts so you can stay on top of your cash requirements.
Cash vs. Accrual Basis
It might help your business decision-making to convert your books from cash basis to accrual basis. This is a huge decision that should be made with an accounting and tax expert, as there are plenty of ramifications to discuss. 
In some cases, the accrual basis of accounting will help keep those annual payments from sneaking up on you as 1/12 of the payment can be accrued on a monthly basis to a payables account. This also keeps your net income figure steadier from month to month.
If your clients prepay their accounts on a yearly basis, you can book the income monthly and keep the difference in a Prepaid account. This spreads your revenues out and recognizes them over time.
“Hiding” Money
If you feel accrual basis accounting is a little too much of a commitment, your accountant can still work with you to help you avoid the impulse of spending too much during the cash-rich busy season. Perhaps the excess cash can be put into a  savings account until it’s needed. You can draw out 1/12 each month as you need it. A little planning such as the above suggested forecasts will help you determine how much you can take out each month. You can even name the Savings account “Do Not Spend!” or “Save for a Rainy Day.”
savings account until it’s needed. You can draw out 1/12 each month as you need it. A little planning such as the above suggested forecasts will help you determine how much you can take out each month. You can even name the Savings account “Do Not Spend!” or “Save for a Rainy Day.”
If it’s just too tempting to have all that excess cash building up in the good times of the year, try one of the ideas above to take back cash flow control and smooth out those bumps.
Does Your Accounting Department Have Holes in It?
You’ve got someone to do your federal and state income tax returns, and you have a bookkeeper. So that’s all that a small business needs when it comes to having an accounting department, right?
Wrong.
Large companies have many functions in their accounting departments, and small and mid-sized businesses need many of the same functions as well. They just won’t need as many staff to handle them. Many of these functions will fall on the CEO, but a smart CEO will find a way to delegate some of the accounting duties to free their time up.
Here are just a few of the things you’ll want to make sure that you have covered in your small business accounting department:
Accounting Software Expertise
Who do you have on your team that can identify opportunities for making your accounting function run more efficiently? The solutions could include training on your current system or could be more comprehensive such as identifying a new accounting system that will save a tremendous amount of time and money.
Let your accountant get to know your processes because they may know of some software applications that can do what you need faster, better, and cheaper. Manual data entry is a hot spot of potential; today, you can find software, scanners, and even smartphones and tablets that can automate the data entry, even if all you have is paperwork to enter.
Business Performance Advice
Are you getting accounting reports that tie to the areas where you have challenges and issues? If not, let your accountant know where those areas are. They may be able to suggest some reports that will provide you with insight and enlightenment.
If you are receiving reports with lots of numbers that you’re not quite sure how to interpret, ask your accountant for help. They can not only help you interpret the numbers, but they can also put the report into a graphical format so that it’s more visual for you.
It’s All About the Revenue
The number one challenge of most small businesses is to attract more business and generate more revenue. Your accountant can help you study your revenue patterns by presenting “what if” tools that can help you see what happens when you change price, impact mix, or adjust volume.
Keeping the Cash Flowing
If your business seems to stampede through cash, you’re not alone. A cash flow forecasting report is in order so you can plan ahead and be ready for the valleys and hills.
Beyond Compliance
If your accounting department focuses on compliance work alone, such as taxes and recordkeeping, you’ll miss out on allowing it to become a profit center of sorts. With these added functions, you’ll discover new actions to take in your business to drive profitability. You’ll have clarity about decisions like price changes, and you’ll know your accounting function is efficient and not wasting time and money.
Take a look at your accounting department, and let us know if we can help you plug any of the holes.
Both the Desktop and Online versions of QuickBooks maintain an Audit Log showing a history of activity in the file by user.
QuickBooks Online Accountant allows you to see all of your QuickBooks Online accounts listed in one login screen and you can choose which client file to access.
Recently, we have witnessed several cross-overs of usernames in the Audit Logs. For example, you could be working in QuickBooks Online as yourself (the Accountant) on Client A, but the Audit Log shows you logged in as Client B on Client A’s file. If Client A happens to check the Audit Log, this could cause quite an alarm!
Unfortunately, there is nothing you can do to change the username retroactively in the Audit Log. There are, however, ways to fix this if it is happening now, and ways to prevent it from happening in the future.

If you have access to multiple QuickBooks Online companies, review the Audit Log in each company. If you log into QuickBooks Online as yourself, and the Audit Log lists another user’s name, this is where you will need to edit your Username record. To edit your username record in any of your QuickBooks Online company logins, go to https://www.login.quickbooks.com/.
Once logged in, you will see a drop-down menu of QBO companies that you have access to. After selecting the company with the incorrect username, you can edit that username to correct the issue going forward.
When you access a new QBO Company, it is always a good idea to check the Audit Log firsthand to prevent future issues.
We have notified Intuit Support of these Realm issues as have other ProAdvisors, and we are awaiting their solution. In the meantime, you may wish to reach out to your affected clients proactively.
 The balance sheet is one of the main financial reports for any business. Among other things, it shows what a company owns, what they owe, and how much they and others have invested in the business. One of the characteristics of a balance sheet is how it separates what you own and what you owe into two categories based on timeframe. The balance sheet is one of the main financial reports for any business. Among other things, it shows what a company owns, what they owe, and how much they and others have invested in the business. One of the characteristics of a balance sheet is how it separates what you own and what you owe into two categories based on timeframe.
Current and Long-Term You may have seen the Assets section of your balance sheet divided into two sections: Current Assets and a list of long-term assets that might include Property, Plant, and Equipment, Intangibles, Long-Term Investments, and Other Assets. Current Assets
Long-Term Assets The remaining assets are long-term, or assets that cannot easily be converted to cash within a year. Property, Plant, and Equipment, also termed Fixed Assets, includes buildings, automobiles, and machinery that the business owns. You might also see an account called Accumulated Depreciation; it reflects the fact that fixed assets lose their value over time and adjusts the balance accordingly. Int Current Liabilities Similarly, liabilities are broken out into the two categories, current and long-term. Current liabilities is made up of credit card balances, unpaid invoices due to vendors (also called accounts payable), and any unpaid wages and payroll taxes. If you have borrowed money from a bank or mortgage broker, the loan will show up in two places. The amount due within one year will show up in current liabilities and the amount due after one year will show up in long-term liabilities. Long-Term Liabilities The most common types of long-term liabilities are notes payable that are due after one year, lease obligations, mortgages, bonds payable, and pension obligations. Why All the Fuss Over Current vs. Long Term?
Next time you receive a balance sheet from your accountant, check out your current and long-term sections so that you’ll gain a better understanding of this report. |
As Accountants we default to the tried and true – the journal entry – we use the traditional system of accounting to record, adjust and correct all things. A debit here, a credit there and voila, we are done.
Not so in QuickBooks® – Journal entries do not use “Items” and items are the backbone of all the subsidiary reports in QuickBooks®. When you run job profitability reports, the costs recorded by journal entries do not show up on the Profit & Loss by Job reports. This holds true for any item-based reports in QuickBooks®.
QuickBooks® likes to have all transactions start with the source document – a Sales Receipt, an Invoice, a Credit Memo, a Payment Receipt, a Deposit, a Bill, a Credit, a Bill Payment, a Check, a Credit Card Charge, a Statement Charge, an Inventory Adjustment, a Sales Tax Adjustment, a Sales Tax Payment, a Payroll Check or a Payroll Liability Payment.
There are very few reasons to create journal entries in QuickBooks® and they should be limited to non-transactional entries with the exception of outsourced payroll.
If you use a third-party payroll service like Paychex® or ADP, the payroll company sends you reports. To record the numbers from those reports into your company file where you need them, you can use journal entries.
You may also need to enter year-end adjustments for Depreciation, Amortization, Prepaid Expenses, Deferred Revenues, Accrued Payroll and Taxes or to allocate Net Income to Partner Equity accounts. These may be done in the form of journal entries and/or reversing entries.
Otherwise, it’s best to use the source documents. Using the forms allows you to maintain the integrity of the management reports like Sales by Customer or Sales by Item.
You should never make journal entries with Accounts Receivable and/or Accounts Payable accounts. While it may clear out the account to zero, you will notice on your Aging Reports that the fixes live forever in the clients’ QuickBooks® file.
Sources and Targets in Journal Entries
All of that being said; I am convinced that some of you are still going to insist on using journal entries for adjusting Accounts Receivable and/or Accounts Payable in QuickBooks®.
With that in mind, a final word of caution – do not use these particular Balance Sheet accounts that require a Customer or Vendor name to be associated with them as the first line in any journal entry.
The first line in a journal entry is the Source of the transaction. All subsequent lines are Targets of the transaction. When you enter a Source Name, QuickBooks® copies that name into any Target Name that you leave blank.
When you make a journal entry in QuickBooks® with Accounts Receivable/Accounts Payable as the first line item and assign a Customer/Vendor Name to that line, each subsequent line uses that Name even if you leave it blank.
For example, let’s say this is the journal entry that you give to your client to enter into their QuickBooks® file to tie out to the year-end trial balance:

This is what QuickBooks does with the transaction behind the scenes:

All lines of the journal entry are associated with the Customer Name “Bill Smith”.
Copying the Source Name creates issues when you filter a report for the Customer: Job Name and the report includes transaction lines that you do not intend; it distorts the report.
To avoid having Customer/Vendor Names incorrectly copied down to the blank lines of an adjustment –
- Enter the accounts with names on the lower lines of the journal entry after the accounts without names, or
- Create a dummy name on the Other Names list e.g. “No Name” and enter it on each of the Target lines.
The Mount Washington Valley Economic Council will be hosting a three-part QuickBooks® Boot Camp series, led by Rhonda Rosand, CPA:
Session #1: Introduction to QuickBooks® Products – What’s Right for Me?
Tuesday, February 24, 2015 – 8:30 AM – 11:00 AM
Whether you are keeping the books for your own business or for others, you need to be using the right tools. We will cover a multitude of options under the Intuit umbrella.
- Desktop Pro and Premier
- Enterprise Solutions and Point of Sale
- Desktop Hosted and Online Solutions
- Payroll – Full Service, Basic, Enhanced, and Assisted
- Third Party Applications
Session #2: QuickBooks® Navigation Workflow and Basic Set Up
Tuesday, March 17, 2015 – 8:30 AM – 11:00 AM
Learn how to navigate your way around the Quickbooks Desktop and online versions, how to begin setting up your own company file and avoid some of the common pitfalls.
- Navigation and Workflow
- Common Pitfalls
- Basic Set Up
Session #3: QuickBooks® Reports and Customizing Forms and Templates
Tuesday, April 7, 2015 – 8:30 AM – 11:00 AM
Learn how to customize forms and templates and create Quickbooks reports that are useful management tools for your business. Understand the difference between profits and cash.
- Customize forms and templates
- Revenue Planning
- Quickbooks Reports
- Cash Flow Management
Courses are $35.00 and are held from 8:30am-11am at:

When you run financial statements on a Cash Basis in QuickBooks®, the results may not be what you expect. For example, you may find balances for Accounts Receivable and/or Accounts Payable on Balance Sheets run on a Cash Basis. This often means that the client has assigned a Payable or a Receivable to a Balance Sheet account, rather than to an Expense or Income account. There are other reasons this happens too.
Reasons for Accounts Receivable on a Cash Basis Balance Sheet
- There may be open balances on Invoices that use Items linked to Balance Sheet accounts. An example would be a Customer Deposit linked to a Liability account.
- There may be a prorata cost of Inventory Items listed on open Invoices. For example, if an Invoice that includes Inventory Part Items is half paid, half the cost of the Inventory Part Items will remain in Accounts Receivable.
- There may be unapplied credits from Credit Memos or Payments. You can find these entries easily because they appear as negative numbers on the Open Invoices report.
- There may be Sales Tax due listed on an accrual basis. You can change the Sales Tax Preference to Cash Basis to eliminate this problem. CAUTION: Check with your State taxing agencies for rules regarding payment of Sales Tax – some States require the basis for Sales Tax accruals to match the basis for Income Tax filing.
Reasons for Accounts Payable on a Cash Basis Balance Sheet
- There may be Bills using Items linked to Balance Sheet accounts.
- There may be Bills entered for a Note Payable or to buy a Fixed Asset.
- You may find the cost of Inventory Part Items on open Bills.
- There may be unapplied Vendor Credits or Prepayments
To review balances in Accounts Receivable and/or Accounts Payable: Filter a transaction report with a paid status of Open transactions and date range of All to get a report showing the transactions that QuickBooks® did not reverse as part of the internal Cash Basis conversion.
- From the Reports menu, choose Company & Financial
- Choose Balance Sheet Standard from the submenu
- Click Customize Report
- Select Cash as the Report Basis
- Click OK
- Double-click the balance in the Accounts Receivable and/or Accounts Payable account
- Click Customize Report, and then click the Filters tab
- In the Filters list, select Paid Status and then select Open
- Click OK
To complete the Cash Basis conversion, use a Journal Entry to adjust away the Accounts Receivable and/or Accounts Payable balances. For the Journal Entry, create a Customer called ***A/R CPA Use Only*** and an Accounts Payable Vendor called ***A/P CPA Use Only***. Use these names to transfer the balances to whatever accounts you choose for the adjustments.
These Journal Entries are Reversing Entries as of the first day in the next fiscal period and you must apply the Journal Entry and the Reversing Entry against each other to offset them or you will have Unapplied Credits going forward.
Do not use Accounts Receivable and/or Accounts Payable as the first line of a journal entry in QuickBooks. See our next Accounting Professionals Only newsletter.
Many Retail stores sell inventory on consignment. It’s important to keep track and to know how much inventory you have in stock, who it belongs to and where it’s all located.
Let’s start our discussion of Accounting for Consignments in QuickBooks with a few basic definitions.
- Consignment – the act of consigning, which is placing any materials in the hands of another.
- Consigned Inventory – the goods shipped by the Consignor to the Consignee.
- Consignor – the owner of the inventory – the person who hands over the goods to be sold.
- Consignee – the seller of someone else’s goods – the person who receives the goods to sell.
There are two sides to the consignment equation – Consignor and Consignee. In this article, we will discuss the situation from the viewpoint of the Consignor. Note: We will also assume that you are using QuickBooks Premier and not Pro or Enterprise.
As the Consignor, you own the inventory – it’s your asset and your responsibility and if the product is damaged, it’s your loss. You are the party at risk and have an insurable asset. You’ve consigned it, or handed it over, to someone else who has agreed to sell it on your behalf in exchange for a pre-determined fee or percentage as well as reimbursable out-of-pocket expenses.
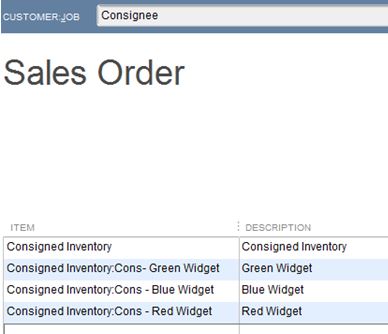
In QuickBooks, it’s as simple as creating a separate section in your Item List for Consigned Inventory and listing each Item as a Sub-Item with an identifier (Cons) that categorizes it as consigned. These are still Inventory Parts and are mapped to the same Cost of Goods Sold, Income and Inventory accounts as your other Inventory Items. Note: You may wish to create a separate Inventory Asset account for your Consigned Inventory, however this is optional.
To transfer the Items from your Regular Inventory to Consigned Inventory, it’s an Inventory Adjustment for Quantity only – the value of your inventory does not change, only the location of the Items for sale. Adjust Inventory/Quantity On Hand is located under the Vendor Menu.
In addition to creating an Inventory Adjustment, you will need to create a Sales Order to the Consignee for the Consigned Inventory. Create Sales Order is located under the Customer Menu. This is a non-posting entry in QuickBooks and will show the Inventory as committed to the Consignee and not available for sale to others on an Inventory Stock Status Report.
As you receive reports of Sales of your Consigned Inventory from the Consignee, or better yet, as you conduct a physical inventory of your Consigned goods at the Retail location, you will create an Invoice in QuickBooks from the Sales Order to the Consignee to bill for your pre-determined percentage of the sale, less reimbursable expenses.
These are the steps to account for Consignments from the perspective of the Consignor.
There are many more steps involved in accounting for Consignments from the angle of the Consignee. We’ll cover these in a later edition of our newsletter – stay tuned.
As always, if you have any questions on any of the procedures for recording Consignments in QuickBooks, please contact us. We’re happy to help.
Accurate, thorough item records inform your customers and help you track inventory levels correctly.
Whether you’re selling one-of-a-kind items or stocking dozens of the same kinds of products, you need to create records for each. When it comes time to create invoices or sales receipts, your careful work defining each type of item will:
- Ensure that your customers receive correct descriptions and pricing,
- Provide the information you must know about your inventory levels, and,
- Help you make smart decisions about reordering.
You’ll start this process by making sure that your QuickBooks file is set up to track inventory. Open the Edit menu and select Preferences, then Items & Inventory. Click the Company Preferences tab and click in the box in front of Inventory and purchase orders are activated if there isn’t a check in the box already. Here, too, you can ask that QuickBooks warn you when there isn’t enough inventory to sell. Click OK when you’re finished.
Figure 1: You need to be sure that QuickBooks knows you’ll be tracking inventory before you start making sales.
To create your first item, open the Lists menu and select Item List. Click the down arrow next to Item in the lower left corner of the window that opens and select New. The New Item window opens.
Warning: You must be very precise when you’re creating item records in order to avoid confusing your customers and creating problems with your accounting down the road. Please call us if you want us to walk you through the first few items.
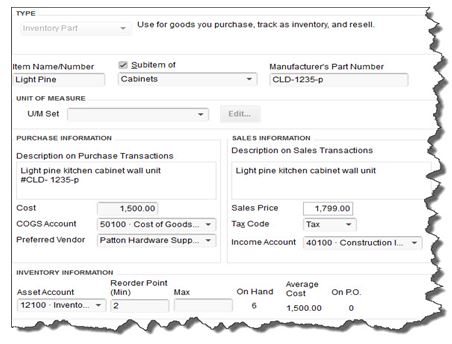
QuickBooks should display the list of options below TYPE. Since you’re going to be tracking inventory that you buy and sell, select Inventory Part. Enter a name and/or item number in the next field. This is not the text that will appear on transactions; it’s simply for you to be able to recognize each item in your own bookkeeping.
Figure 2: Let us work with you if you have any doubts about the data that needs to be entered in the New Item window. It must be 100 percent accurate.
In the example above, the box next to Subitem of has a check mark in it because “Light Pine” is only one of the cabinet types you sell (you can check this box and select <Add New> if you want to create a new “parent” item on the fly). Leave the next field blank if your item doesn’t have a Part Number, and disregard UNIT OF MEASURE unless you’re using QuickBooks Premier or above.
Fill in the PURCHASE INFORMATION and SALES INFORMATION fields (or select from the lists of options). Keep in mind that the descriptive text you enter here will appear on transaction forms, though customers will never see what you’ve actually paid for items, of course (your Cost, as opposed to the Sales Price).
QuickBooks should have automatically selected the COGS Account (Cost of Goods Sold), but you’ll need to specify an Income Account. Please ask us if you’re not sure, as this is a critical designation. The Preferred Vendor and Tax Code fields will display lists if you’ve already set these up.
QuickBooks should have pre-selected your Asset Account. If you want to be alerted when your inventory level for this item has fallen to a specific number (Min) so you can reorder up to the point you specify in the Max field, enter those numbers there (the Inventory to Reorder option must be turned on in Edit | Preferences | Reminders).
If you already have this item in stock, enter the number under On Hand. QuickBooks will automatically calculate Average Cost and On P.O. (Purchase Order).
Click OK when you’ve completed all of the fields. This item will now appear in your Item List, and will be available to use in transactions. When you want to create, edit, delete, etc. any of your items, simply open the same menu you opened in the first step here (Lists | Item List | Item).
Figure 3: The Item menu, found in the lower left corner of the Item List.
Precisely created Inventory Part records are critical to accurate sales and purchase transactions. So use exceptional care in building them.
The technology side of the accounting industry is rapidly changing and expanding. Literally hundreds, if not thousands of new companies and new software applications have sprung up to help small businesses automate their processes and save time and money.
The best way to profit from all of this innovation is to first identify where you can best use the technology in your business. Here are three places to look:
 What business tasks are you still using pen and paper for? Look what’s on your desk or in your filing cabinet in the form of paper, and that will be your next opportunity for automation. For example, are you still hand-writing checks? There’s an app (or two) for that.
What business tasks are you still using pen and paper for? Look what’s on your desk or in your filing cabinet in the form of paper, and that will be your next opportunity for automation. For example, are you still hand-writing checks? There’s an app (or two) for that.
Sticky notes and to do lists have been replaced with Evernote. Business cards you collect can go in a CRM (customer relationship manager). All of your accounting invoices and bills can be digitized and stored online.
Make a list of all the manual and paper processes you do every day and look for an app that can make the task faster for you.
 Take stock of what systems you already have in place. The opportunity to fill the gap is where you might have systems that should talk to each other but don’t. If you need to enter data into two different places, there may be a chance to automate and/or integrate the systems or data. For example, your point of sale or billing system should integrate well with your accounting system. A few other examples include accounting and payroll, CRM and accounting, inventory and accounting, project management and time tracking, and time tracking and payroll.
Take stock of what systems you already have in place. The opportunity to fill the gap is where you might have systems that should talk to each other but don’t. If you need to enter data into two different places, there may be a chance to automate and/or integrate the systems or data. For example, your point of sale or billing system should integrate well with your accounting system. A few other examples include accounting and payroll, CRM and accounting, inventory and accounting, project management and time tracking, and time tracking and payroll.
The more your systems integrate and work as a suite, the better.
 It could be you have your systems automated, but the systems are not the best choice for your business requirements. If your systems don’t meet many of your business requirements, it may be time to look for an upgrade or a replacement.
It could be you have your systems automated, but the systems are not the best choice for your business requirements. If your systems don’t meet many of your business requirements, it may be time to look for an upgrade or a replacement.
If you are performing a lot of data manipulation in Excel or Access, this might also signal that your systems are falling short of your current needs. Look where that’s happening, and you will have identified an opportunity for improvement.
Look in these three areas in your business, and I bet you’ll not only find an app for that, you’ll also find some freed up time and money once you automate.
 New Business Direction LLC
New Business Direction LLC Current Assets include all of the items the business owns that are liquid and can easily be converted to cash within one operating cycle, typically a year’s time. The most common types of current assets include the balances in the checking and savings accounts, receivables due from clients who haven’t paid their invoices, and inventory for resale.
Current Assets include all of the items the business owns that are liquid and can easily be converted to cash within one operating cycle, typically a year’s time. The most common types of current assets include the balances in the checking and savings accounts, receivables due from clients who haven’t paid their invoices, and inventory for resale. angible assets are assets that have value but no physical presence. The most common intangible assets are trademarks, patents, and Goodwill. Goodwill arises out of a company purchase. Investments that are not easily liquidated will also be listed under Long-Term Assets.
angible assets are assets that have value but no physical presence. The most common intangible assets are trademarks, patents, and Goodwill. Goodwill arises out of a company purchase. Investments that are not easily liquidated will also be listed under Long-Term Assets. Bankers and investors want to know how liquid a company is. Comparing current assets to current liabilities is a good indicator of that. Some small businesses have loan covenants requiring that they maintain a certain current ratio or their loan will be called. The current ratio of your business is equal to current assets divided by current liabilities. Bankers like this amount to meet or exceed 1.2 : 1 (that’s 120%: 100%, although this can vary by industry).
Bankers and investors want to know how liquid a company is. Comparing current assets to current liabilities is a good indicator of that. Some small businesses have loan covenants requiring that they maintain a certain current ratio or their loan will be called. The current ratio of your business is equal to current assets divided by current liabilities. Bankers like this amount to meet or exceed 1.2 : 1 (that’s 120%: 100%, although this can vary by industry).