Kristen has earned her designation as a QuickBooks Certified User on November 4, 2013. Kristen has attended extensive training courses on QuickBooks and has been with New Business Directions since December of 2011.
Kristen has earned her designation as a QuickBooks Certified User on November 4, 2013. Kristen has attended extensive training courses on QuickBooks and has been with New Business Directions since December of 2011.
In addition to being a Level One Bookkeeper for New Business Directions, Kristen is also our in-house Marketing Coordinator, and has recently created a blog on our website which features helpful Tips and Tricks in QuickBooks. If you would like to submit a QuickBooks related topic to be covered in our blog, email Kristen at Kristenp@newbusinessdirections.com.
At New Business directions we help small business owners streamline the process of making money. If you would like to create order out of chaos and improve your bottom line, call us at 603-356-2914 or visit our website at www.newbusinessdirections.com.
New version of desktop QuickBooks accomplishes goal of speeding up, refining your workflow.
If Intuit named its desktop versions of QuickBooks by the version number rather than the year, we’d be in version 20-something by now. QuickBooks, still the preferred software for small businesses, keeps getting smarter in its annual upgrades. Rather than pile on tons of new features in its upgrades, Intuit – for many years – has concentrated on making it easier for you to access the tools and data that are already there.
QuickBooks 2014 is no exception. Its combination of small-but-effective changes makes it easier to get in and do what needs to be done quickly, and then get out and move on to activities that will help build your business.
A Superior View
If you do upgrade to QuickBooks 2014, head first to the new Income Tracker (Customers | Income Tracker). QuickBooks offers numerous reports and other tools for following the progress of your incoming revenue, but this new feature provides the best we’ve seen in the software.
Figure 1: QuickBooks 2014’s new Income Tracker gives you real-time access to the status of your receivables.
You may find yourself spending a lot of time on this screen because it gives you a birds-eye view of your receivables that isn’t available anywhere else in the program. You can click on any of the four colored bars that run across the top of the screen – Estimates, Open Invoices, Overdue and Paid Last 30 Days — to change the data that appears below. Within each bar is the number of related transactions and their total dollar amount.
You’ll use the drop-down lists directly below these navigational bars to set filters that define a subset of transactions. These are CUSTOMER:JOB, TYPE, STATUS and DATE.
The last column in the table is labeled ACTION. Once you’ve earmarked a transaction or transactions that you want to work with by checking the box in front of each name, you can select an action you want to take. If OPEN INVOICES is active, for example, you can receive payment for the transaction(s), print or email them. Where applicable, you can open a drop-down menu in the lower left of the screen and batch-produce invoices, sales receipts and credit memos/refunds.
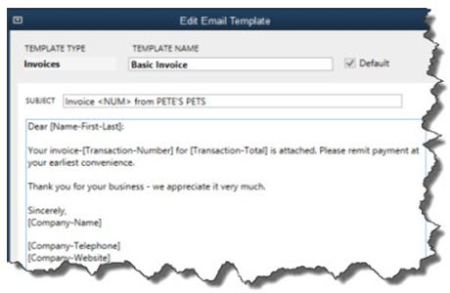
More Descriptive Email
If you regularly send invoices through email, you may have wondered how many of them actually get opened by your customers in a timely fashion. QuickBooks 2014 contains a new tool that makes the details of each invoice available within the body of the email itself.
Figure 2: You can modify this template or leave it as is: QuickBooks 2014 will fill in the relevant details for each customer.
To access this template, open the Edit menu and select Preferences. Click on the Send Forms tab, then Company Preferences. Open the drop-down list to select the type of form you want to view or modify (pay stub, sales receipt, credit memo, etc.). Click the Edit button to see the actual template, and open the Insert Field drop-down menu to see your options. When you email a form, QuickBooks will replace the text and numbers in brackets with the correct details for each recipient.
This is what’s called a mail merge. They’re fairly simple to use, but one error will throw your message off. We can help you get set up with these.
Smaller Changes
Intuit has made many small-but-useful features to QuickBooks 2014, all designed to help you work faster and smarter, and simply to support more convenient operations. For example, the Ribbon toolbars on transactions now include a tab or menu that lets you open related reports.
Figure 3: You can now access reports directly from the Ribbon toolbar on transaction screens.
In addition:
- QuickBooks’ color scheme has been changed.
- The program runs faster.
- You can now copy and paste lines within forms.
- We can communicate with you (and vice versa) via an email window that’s been embedded into the software. This tool even auto-pastes the transaction in question into the email window.
- There’s been some retooling of online banking (now called “Bank Feeds”), making it more accessible and understandable.
Upgrading to a new version of QuickBooks can be challenging, so we encourage you to let us know if you’d like to explore the process. New functionality and usability that improves your workflow and your understanding of your finances can be worth the time and trouble.
If QuickBooks were just one product, its appeal would be more limited than it is. Because there’s an entire family of Windows desktop software applications (as well as five online versions and a Mac edition), the QuickBooks family has found a home in

millions of small businesses, and it remains the market leader. Though QuickBooks versions themselves are not scalable (able to expand as your business grows), you can move up to a more sophisticated edition when you outgrow your current version.
But how do you know whether it’s time to upgrade or whether you’re just not stretching your current version to its fullest capabilities? We can help you determine that, and we’ll help you move into a more appropriate edition when/if that occurs.
Desktop Differences
There are three Windows-based versions of QuickBooks: Pro, Premier and Enterprise Solutions. They all let you:
Figure 1: All desktop versions of QuickBooks let you import and export data.
All three versions share a similar user interface and navigational scheme, so when you move up to the next level, you only need to learn the new features. The 2013 offerings make it even easier to learn and use QuickBooks, since Intuit completely revamped the look and feel for those most current editions. QuickBooks Pro is the base desktop product, offering everything in the above list and more. But would you rather have access to 150+ reports instead of 100, including some that are industry-specific? QuickBooks Premier can provide that, in addition to charts of accounts, sample files and menus tailored to your company’s industry. It also offers a business plan builder and the ability to forecast sales and expenses.
Figure 2: QuickBooks Premier helps you create a business plan. The biggest jump in functionality, though, occurs when you move up to QuickBooks Enterprise Solutions. You may want to consider this upgrade when you find that, for example:
|
Robust Accounting
|
QuickBooks Enterprise Solutions is well-suited to complex small businesses, and sometimes even larger companies, depending on their structure and needs. It solves the data management problems that Pro and Premier users can experience, thanks to its 100,000+ record and account capacity.
Up to 30 individuals can use the software at the same time, and they have more flexibility than is offered in Pro and Premier. Multiple users can be on the system and still complete tasks like adjusting inventory and changing sales tax rates. You can manage more than one business using QuickBooks Enterprise Solutions, even working in two company files at the same time and combining reports. Reporting capabilities themselves are much more sophisticated: The Intuit Statement Writer helps you create professional financial statements, and you have much more control over customization of your output.
Figure 3: QuickBooks Enterprise Solutions offers more sophisticated inventory management tools than Pro or Premier. Inventory management goes many steps further in this sophisticated software. It supports management of multiple warehouse and trucks, and allows transfers among them. Finding specific items is much easier because you can track down to the bin level. FIFO costing is offered as an alternative to average costing, and you can scan items and serial numbers directly into QuickBooks Enterprise Solutions, which tracks both serial and lot numbers. |
This article of QuickBooks Tips and Tricks was based on the 2013 version of QuickBooks.
 We are pleased to announce that we have relocated our existing office from Echo Acres to our new space at:
We are pleased to announce that we have relocated our existing office from Echo Acres to our new space at:
3641-B White Mountain Highway
North Conway, NH
Our new office is located directly across from the Intervale Scenic Vista.
Our mailing address, business telephone and fax numbers will remain the same.
We look forward to being of continued service to you and I hope you will enjoy the benefits of our company at our new office location.
Greetings!
QuickBooks is easy to use, intuitive and flexible. But it is not an accounting manual or class or tutorial. If your business is exceptionally uncomplicated, you might get by without knowing a lot about the principles of bookkeeping.
Still, it helps to understand the basics. Here’s a look at some terms and phrases you should understand.

2. Accounts Payable (A/P). Everything that you owe to vendors, contractors, consultants, etc. is tracked in this account.
3. Accounts Receivable (A/R). This account tracks income that hasn’t been realized yet, like outstanding invoices.
4-5. Accrual Basis. This is one of two basic accounting methods. Using it, you record income as it is invoiced, not when it’s actually received, and you record expenses like bills when you receive them. Using the other method, Cash Basis, you would report income when you receive it and expenses when you pay the bills.
6-7 Asset. What physical items do you own that have value? This could be cash, office equipment and real estate. In QuickBooks you’ll be managing two types. Current Assets are generally used within 12 months (or you could convert them to cash in that length of time). Fixed Assets refers to belongings like vehicles, furniture and land, property that you probably won’t use up in a year and which usually depreciates in value. Depreciation is very complex; you may need our help with that.
8. Average Cost. This is the inventory costing method that programs like QuickBooks Pro and Premier use to calculate the value of your stock.

10-12. Double-Entry Accounting.This is the system that QuickBooks uses – that all legitimate small business accounting software uses. Every transaction must show where the funds came from and where they went. Each has a Credit (decreases asset and expense accounts) and Debit (decreases liability and income accounts) which must balance out (other types of accounts can be affected).13. Equity.This refers to your company’s net worth. It’s the difference between your assets and liabilities.
14. General Journal. QuickBooks handles this in the background, so it’s unlikely you’ll ever be exposed to it. We sometimes have to create General Journal Entries, transactions required for various reasons (errors, depreciation, etc.) that contain debits and credits. Please leave that to us.
15. Item Receipt. You’ll create these when you receive inventory from a vendor without a bill.
16. Job. QuickBooks often associates customers with multi-part projects that you’ve taken on, like a kitchen remodel.
17. Net income. This is your revenue minus expenses.
18. Non-Inventory Part. When you purchase an item but don’t sell it or you buy something and resell it immediately to a customer, this is what it’s called. It’s merchandise that isn’t stored by you for future sales.
19. Payroll Liabilities Account. QuickBooks tracks federal, state and local withholding taxes, as well as Social Security and Medicare obligations, that you’ve deducted from employees’ paychecks and will remit to the appropriate agencies.

20. Post.You won’t run into this term in QuickBooks. It simply refers to recording a transaction within one of your accounts.
21. Reconcile. QuickBooks helps you with this. It’s the process of making sure your records and those of your financial institutions agree.
22. Sales Receipt.This is how you record a sale when payment is made in full during the transaction.
23. Statement. You’ll generally use invoices to bill customers in QuickBooks, but you can also send statements, which contain transaction information for a given date range.
24. Trial Balance. This standard financial report tells you whether your debits and credits are in balance. Should you run this report and find a problem, let us know right away.
25. Vendor. With the exception of employees, QuickBooks uses this term to refer to anyone who you pay as a part of your business operations.
These are just a few of the terms you should recognize and understand. We hope you’ll contact us when you need help understanding how the accounting process fits into your workflow.
 New Business Direction LLC
New Business Direction LLC