QuickBooks is made up of Lists. The most important list in QuickBooks is the Chart of Accounts; it creates the framework for your financial reports from your Balance Sheet to your Profit and Loss statement and your statement of cash flows. It also creates the infrastructure for your budgets or revenue plan.
Learn about the Chart of Accounts in QuickBooks with Rhonda Rosand, CPA or New Business Directions, LLC.
Each January we rush around to gather tax information on the independent contractors we paid in the prior year in order to send them a 1099. Here are some basic tips for making it easier and less hurried in your year-end preparations.
A link to the IRS’s instructions for 2018 can be found here.
Form W-9
As a trade or business, you are required to obtain a Form W-9 from your independent contractors before you pay them, better yet – before they do any work for you. This is regardless of how much money you pay them. This form will give you the name, business name, address, entity type and taxpayer identification number.
Who Needs a 1099?
Service Providers – Anyone you pay in the course of your trade or business for services rendered. This includes Accountants, Consultants, Architects, Engineers, Designers, Contractors, Plumbers, Electricians, Installers, Landscapers, Snow Removal companies, Cleaning companies, the Auto Repair technician, Entertainers – anyone who performs a service or casual labor for your business who is not your employee.
Rents – If your business pays rent for office space or land or equipment, you are required to send the recipient a 1099 for the amount of rent you have paid them.
Exclusions – Sole proprietorships, partnerships and LLC’s that are taxed as sole proprietors and/or partnerships receive a 1099. You are not required to send 1099’s to a Corporation or a Tax Exempt entity. The Form W-9 will provide information regarding the entity type.
Threshold – Send to recipients to whom you have paid $600 or more during the calendar year.
Using the QuickBooks® 1099 Wizard
QuickBooks® has a 1099 Wizard to create accurate 1099 and 1096 forms. It allows you to review and edit  your vendors, set up account mapping preferences, run a summary report to review data, and print 1099 and 1096 forms.
your vendors, set up account mapping preferences, run a summary report to review data, and print 1099 and 1096 forms.
Note: QuickBooks® is only capable of preparing 1099-MISC. If you need to prepare other types of 1099’s (e.g. 1099-INT, 1099-DIV), you will need to do so outside of QuickBooks®.
Deadline
For 2018, if you are reporting Non Employee Compensation in Box 7, you are required to file on or before January 31, 2019 to both the recipients and to the Internal Revenue Service.
New Business Directions, LLC specializes in QuickBooks® set up, clean up, consulting and training services, coaching small business owners and providing innovative business solutions.
This article of QuickBooks Tips and Tricks was based on the 2018 version of QuickBooks®.
The Mt. Washington Valley Economic Council
FALL 2018
QuickBooks® Desktop Boot Camps
with Rhonda Rosand, CPA – Advanced Certified QuickBooks® ProAdvisor
Session #1 QuickBooks® Set Up – Do It Right the First Time
Tuesday, October 2nd, 2018, 9 AM -11 AM
Whether you are starting from scratch or starting over, there is a right way and several wrong ways to set up a QuickBooks® file. Learn how to do it right the first time.
Avoid some of the common mistakes we see people make.
QuickBooks® Solutions
Accounts and Items
Users and Permissions
Customers/Jobs/Vendors
Class Tracking
Common Pitfalls
Session #2 Customizing Forms and Templates and QuickBooks® Reports
Tuesday, October 16th, 2018, 9 AM – 11 AM
Learn how to customize forms and templates and create QuickBooks® reports that are useful management tools for your business. Understand the difference between profits and cash.
Customize Forms and Templates
QuickBooks Reports
Revenue Planning
Cash Flow Management
Tuesday, October 23rd, 2018, 9 AM-NOON
This is a session designed exclusively for tax preparers, enrolled agents and accountants. We will cover advanced level topics to help you streamline the process and best practices for troubleshooting your client QuickBooks® file during this busy tax season.
What’s New in QuickBooks® 2019
In Product Demonstration of Features
Client Data Review and Accountant Toolbox
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Hosting Platforms
3rd Applications
Courses are $35 each and held in the Community Room at Granite State College-Conway.
To register please call Susie at (603) 447-6622, email susie@mwvec.com, or register online.
QuickBooks 2016 offers some new features that we are excited to share with our fellow accounting professionals. Batch Delete/Void Transactions and enhanced Statement Writer Support are two of the latest features available to Accountants only. Sorting on Item Custom Fields and Auto Copy Ship to Addresses are features only available in Premier (including Accountant) and Enterprise versions of the software.
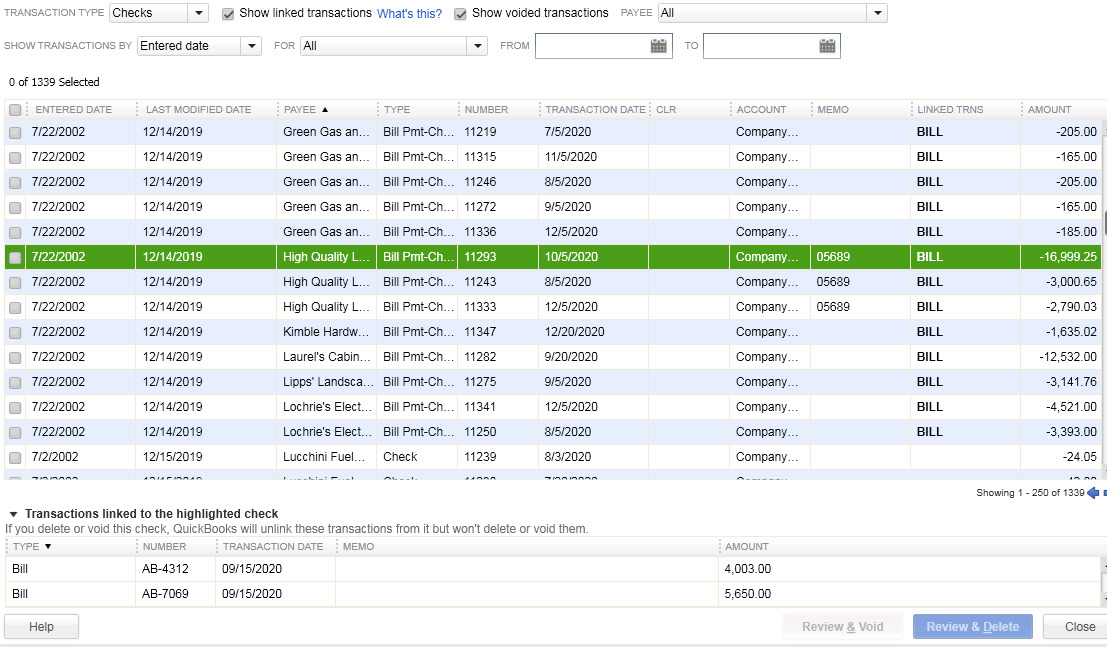
Batch Delete/Void Transactions
We are cautiously excited about this new feature as it could prove to be quite dangerous in the wrong hands. Fortunately, Intuit realized that and only made the tool available in the Accountant and Enterprise versions of the software and in the Accountant Toolbox in the Pro and Premier versions.
It works for Invoices, Bill and Check transactions, but not for Credit Cards Charges or Deposits, at this time. It is also not available for Payroll or Sales Tax Transactions. The columns can be sorted by Entered Date, Modified Date or Transaction Date as well as by Payee, Type, Number, Account or Amount.
Any other transactions that are linked to the transaction to be voided/deleted are highlighted for you to be aware and to address them as well, if need be. For example, voiding a Bill-Check does not void the related Bill.
I am hopeful that Intuit will improve this feature and add the ability to work with Credit Card Charges, as I have seen many occasions where these were imported to the wrong account or even twice to the same account. As with any tool of this nature, we recommend a backup before and to Void instead of Delete.
Statement Writer Support for Microsoft Office
I do not prepare financial statements, but for those who do and for those who use the QuickBooks Statement Writer, it is essential to have the integration with Microsoft Word and Excel. With QuickBooks 2016, we have this integration with the Accountant and Enterprise versions of the software. However, we still do not have support for the cloud-based Microsoft Office 365.
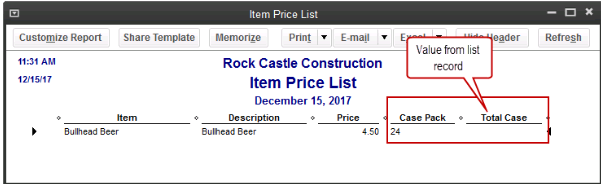
Sorting on Item Custom Fields
In prior versions, we had the ability to sort on the Customer and Vendor Custom Fields, but not on the Items Custom Fields – those fields were mostly notational and not very reportable.
In QuickBooks 2016 Premier, Accountant, and Enterprise, Intuit introduced this feature which will allow sorting on Inventory Valuation and Inventory Stock Status reports as well as the Inventory Price List. This will save countless hours of exporting to Excel and creating Pivot Tables to gather the required information.
Auto Copy Ship to Addresses
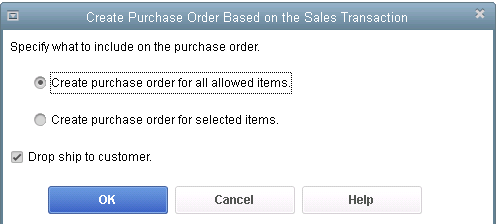
For Contractors and Retailers who order materials or goods to be shipped directly to the job site or customer, QuickBooks 2016 – Premier, Accountant and Enterprise, has the ability to populate the Customer address in the Ship To Address directly from an Estimate or Sales Order, simply by selecting the Drop Ship to Customer checkbox when creating a Purchase Order.
We are pleased to announce that on November 18th, 2015, Rhonda Rosand, CPA/Owner of New Business Directions, will be conducting the QuickBooks 2016 Expanded workshop sponsored by the New Hampshire Society of Accountants at the Executive Court in Manchester, NH.
Rhonda will touch on What’s New in QuickBooks 2016, how to fully utilize QuickBooks, which software program works best for you and your clients, and an accountants only section leaving plenty of time for questions.
Registration fee is $89 for NHSA members and $109 for non-members and allows participants to earn 4 CPE credits. To sign up for this event, please call (603)228-1231 or email info@cornerstoneam.com

On November 2nd– 4th, Intuit will be hosting the 2nd annual QuickBooks Connect Conference in San Jose. The conference brings together thousands of entrepreneurs, small business owners, accounting professionals and developers  under one roof.
under one roof.
There are three different tracks on the agenda as follows:
Accountant – QuickBooks Connect will help your firm get future ready by challenging you to go further, think differently, and embrace the cloud to properly value the services you provide, grow your firm, and better support your clients. *
Small Business – Whether you’re a company of one or one hundred, come to make your business dream a reality: network with fellow small business owners, entrepreneurs, self employed individuals, startup founders, and Venture Capital leaders to receive personalized advice on maximizing your success. *
Developer – Engage Intuit Developer experts to speed your QuickBooks app integration and successful launch to the QuickBooks ecosystem. Take advantage of the unique opportunity to meet and network with other developers, accountants and small business owners. *
The mission is to connect, learn and grow throughout a dynamic agenda of main stage and intimate sessions. Key speakers  include Oprah Winfrey, Jessica Alba, Brian Lee and Robert Herjavec. Sessions topics include: Here to There: The Accountant’s Journey toward Professional Greatness, Work/Life Harmony, 10 Barriers to Service Excellence and How to Overcome Them, and Cash is King: Tips to Increase Your Cash Flow Today. There will also be speed mentoring sessions and an entire series of QuickBooks Online training topics.
include Oprah Winfrey, Jessica Alba, Brian Lee and Robert Herjavec. Sessions topics include: Here to There: The Accountant’s Journey toward Professional Greatness, Work/Life Harmony, 10 Barriers to Service Excellence and How to Overcome Them, and Cash is King: Tips to Increase Your Cash Flow Today. There will also be speed mentoring sessions and an entire series of QuickBooks Online training topics.
Rhonda Rosand states, “This will be my second year attending the Intuit conference and I look forward to seeing many familiar faces at the event and I invite you to join me in California for this spectacular training opportunity.”
* – content is taken directly from the QuickBooks Connect Website
As we move into the fall season and the final quarter of the year, it’s a perfect time to commit to a project in your business that will help you reach the year’s end in better shape. Here are five ideas:
1. Back-to-School Time
If payroll expenses are one of the higher costs in your business, then it makes sense to boost your team’s productivity and maybe also your own. Fall is back-to-school time anyway, so it’s a natural time of the year to take on a course, read a business book, or hire an organizer to help you get more from your workspace.
If you spend a lot of time doing email, consider taking a course on Microsoft Outlook® or even Windows; learning a few new keystrokes could save you tons of time. If you need more time, look for a book or course on time management. Look for classes at your local community college or adult education center.

2. A Garage Sale for Your Business
Do you have inventory in your business? If so, take a look at which items are slower-moving and clear them out in a big sale. We can help you figure out what’s moving slowly, and you might even save on taxes too.
3. Celebrate Your Results
Take a checkpoint to see how your revenue and income are running compared to last year at this time. Is it time for a celebration, or is it time to hunker down and bring in some more sales before winter? With one more quarter to go, you have time to make any strategy corrections you need to at this time. Let us know if we can pull a report that shows your year-on-year financial comparison.
4. Get Ready for Year’s End
Avoid the time pressure of year’s end by getting ready early. Review your balance sheet to make sure your account balances are correct for all transactions entered to date. You will be ahead of the game by getting the bulk of the year reviewed and out of the way early.
Also make sure you have the required documentation you need from vendors and customers. One example is contract labor that you will need to issue a 1099 for; make sure you have a W-9 on file for them. If we can help you get ready for year-end, let us know.
5. Margin Mastery
If your business has multiple products and services, there may be some that are far more profitable than others. Breaking these numbers out to calculate your profit margins or contribution margins by product or service line can help you see the areas that are adding the most income to your bottom line. Correspondingly, you can determine if you have any items that are losing money; knowing will help you take the right action in your business. Refresh your financials this fall with your favorite idea of these five, or come up with your own fall project to rejuvenate your business.
contribution margins by product or service line can help you see the areas that are adding the most income to your bottom line. Correspondingly, you can determine if you have any items that are losing money; knowing will help you take the right action in your business. Refresh your financials this fall with your favorite idea of these five, or come up with your own fall project to rejuvenate your business.
 The balance sheet is one of the main financial reports for any business. Among other things, it shows what a company owns, what they owe, and how much they and others have invested in the business. One of the characteristics of a balance sheet is how it separates what you own and what you owe into two categories based on timeframe. The balance sheet is one of the main financial reports for any business. Among other things, it shows what a company owns, what they owe, and how much they and others have invested in the business. One of the characteristics of a balance sheet is how it separates what you own and what you owe into two categories based on timeframe.
Current and Long-Term You may have seen the Assets section of your balance sheet divided into two sections: Current Assets and a list of long-term assets that might include Property, Plant, and Equipment, Intangibles, Long-Term Investments, and Other Assets. Current Assets
Long-Term Assets The remaining assets are long-term, or assets that cannot easily be converted to cash within a year. Property, Plant, and Equipment, also termed Fixed Assets, includes buildings, automobiles, and machinery that the business owns. You might also see an account called Accumulated Depreciation; it reflects the fact that fixed assets lose their value over time and adjusts the balance accordingly. Int Current Liabilities Similarly, liabilities are broken out into the two categories, current and long-term. Current liabilities is made up of credit card balances, unpaid invoices due to vendors (also called accounts payable), and any unpaid wages and payroll taxes. If you have borrowed money from a bank or mortgage broker, the loan will show up in two places. The amount due within one year will show up in current liabilities and the amount due after one year will show up in long-term liabilities. Long-Term Liabilities The most common types of long-term liabilities are notes payable that are due after one year, lease obligations, mortgages, bonds payable, and pension obligations. Why All the Fuss Over Current vs. Long Term?
Next time you receive a balance sheet from your accountant, check out your current and long-term sections so that you’ll gain a better understanding of this report. |
The Mount Washington Valley Economic Council will be hosting a three-part QuickBooks® Boot Camp series, led by Rhonda Rosand, CPA:
Session #1: Introduction to QuickBooks® Products – What’s Right for Me?
Tuesday, February 24, 2015 – 8:30 AM – 11:00 AM
Whether you are keeping the books for your own business or for others, you need to be using the right tools. We will cover a multitude of options under the Intuit umbrella.
- Desktop Pro and Premier
- Enterprise Solutions and Point of Sale
- Desktop Hosted and Online Solutions
- Payroll – Full Service, Basic, Enhanced, and Assisted
- Third Party Applications
Session #2: QuickBooks® Navigation Workflow and Basic Set Up
Tuesday, March 17, 2015 – 8:30 AM – 11:00 AM
Learn how to navigate your way around the Quickbooks Desktop and online versions, how to begin setting up your own company file and avoid some of the common pitfalls.
- Navigation and Workflow
- Common Pitfalls
- Basic Set Up
Session #3: QuickBooks® Reports and Customizing Forms and Templates
Tuesday, April 7, 2015 – 8:30 AM – 11:00 AM
Learn how to customize forms and templates and create Quickbooks reports that are useful management tools for your business. Understand the difference between profits and cash.
- Customize forms and templates
- Revenue Planning
- Quickbooks Reports
- Cash Flow Management
Courses are $35.00 and are held from 8:30am-11am at:

Many Retail stores sell inventory on consignment. It’s important to keep track and to know how much inventory you have in stock, who it belongs to and where it’s all located.
Let’s start our discussion of Accounting for Consignments in QuickBooks with a few basic definitions.
- Consignment – the act of consigning, which is placing any materials in the hands of another.
- Consigned Inventory – the goods shipped by the Consignor to the Consignee.
- Consignor – the owner of the inventory – the person who hands over the goods to be sold.
- Consignee – the seller of someone else’s goods – the person who receives the goods to sell.
There are two sides to the consignment equation – Consignor and Consignee. In this article, we will discuss the situation from the viewpoint of the Consignor. Note: We will also assume that you are using QuickBooks Premier and not Pro or Enterprise.
As the Consignor, you own the inventory – it’s your asset and your responsibility and if the product is damaged, it’s your loss. You are the party at risk and have an insurable asset. You’ve consigned it, or handed it over, to someone else who has agreed to sell it on your behalf in exchange for a pre-determined fee or percentage as well as reimbursable out-of-pocket expenses.
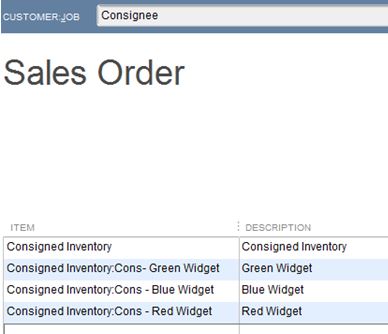
In QuickBooks, it’s as simple as creating a separate section in your Item List for Consigned Inventory and listing each Item as a Sub-Item with an identifier (Cons) that categorizes it as consigned. These are still Inventory Parts and are mapped to the same Cost of Goods Sold, Income and Inventory accounts as your other Inventory Items. Note: You may wish to create a separate Inventory Asset account for your Consigned Inventory, however this is optional.
To transfer the Items from your Regular Inventory to Consigned Inventory, it’s an Inventory Adjustment for Quantity only – the value of your inventory does not change, only the location of the Items for sale. Adjust Inventory/Quantity On Hand is located under the Vendor Menu.
In addition to creating an Inventory Adjustment, you will need to create a Sales Order to the Consignee for the Consigned Inventory. Create Sales Order is located under the Customer Menu. This is a non-posting entry in QuickBooks and will show the Inventory as committed to the Consignee and not available for sale to others on an Inventory Stock Status Report.
As you receive reports of Sales of your Consigned Inventory from the Consignee, or better yet, as you conduct a physical inventory of your Consigned goods at the Retail location, you will create an Invoice in QuickBooks from the Sales Order to the Consignee to bill for your pre-determined percentage of the sale, less reimbursable expenses.
These are the steps to account for Consignments from the perspective of the Consignor.
There are many more steps involved in accounting for Consignments from the angle of the Consignee. We’ll cover these in a later edition of our newsletter – stay tuned.
As always, if you have any questions on any of the procedures for recording Consignments in QuickBooks, please contact us. We’re happy to help.
 New Business Direction LLC
New Business Direction LLC

 Current Assets include all of the items the business owns that are liquid and can easily be converted to cash within one operating cycle, typically a year’s time. The most common types of current assets include the balances in the checking and savings accounts, receivables due from clients who haven’t paid their invoices, and inventory for resale.
Current Assets include all of the items the business owns that are liquid and can easily be converted to cash within one operating cycle, typically a year’s time. The most common types of current assets include the balances in the checking and savings accounts, receivables due from clients who haven’t paid their invoices, and inventory for resale. angible assets are assets that have value but no physical presence. The most common intangible assets are trademarks, patents, and Goodwill. Goodwill arises out of a company purchase. Investments that are not easily liquidated will also be listed under Long-Term Assets.
angible assets are assets that have value but no physical presence. The most common intangible assets are trademarks, patents, and Goodwill. Goodwill arises out of a company purchase. Investments that are not easily liquidated will also be listed under Long-Term Assets. Bankers and investors want to know how liquid a company is. Comparing current assets to current liabilities is a good indicator of that. Some small businesses have loan covenants requiring that they maintain a certain current ratio or their loan will be called. The current ratio of your business is equal to current assets divided by current liabilities. Bankers like this amount to meet or exceed 1.2 : 1 (that’s 120%: 100%, although this can vary by industry).
Bankers and investors want to know how liquid a company is. Comparing current assets to current liabilities is a good indicator of that. Some small businesses have loan covenants requiring that they maintain a certain current ratio or their loan will be called. The current ratio of your business is equal to current assets divided by current liabilities. Bankers like this amount to meet or exceed 1.2 : 1 (that’s 120%: 100%, although this can vary by industry).