- Discourage employees from excessive web browsing. This can be a hard rule to enforce, as some employees probably need internet access for research, timecard entry, and other work-related tasks. Create a firm policy legislating what workers can and can’t do on company-issued equipment (including tablets and smartphones) or any personal devices that use your wireless network.
- Ask employees to refrain from using public networks on work equipment. Enforce the rules vigorously, and make compliance an element of performance evaluations.
- Minimize app installations on business smartphones. Employees should ask for approval. Viruses and malware get in that way, as well as through some websites and email attachments.
- Use monitoring software. If you can’t afford to pay for “managed IT” (a la carte, third-party IT services), install an application that alerts you to problems.
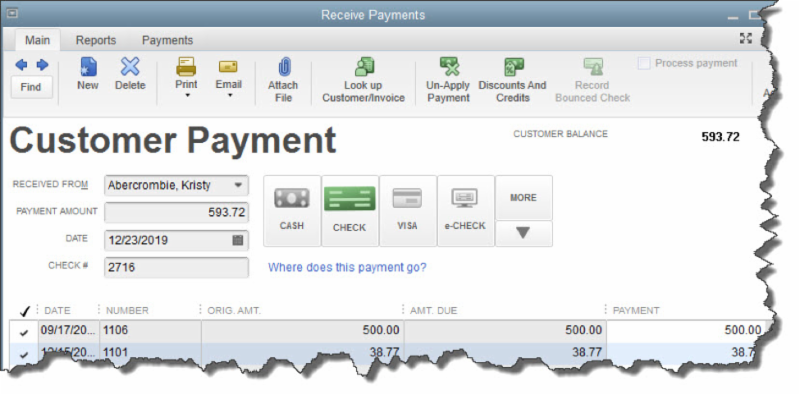
- CASH
- CHECK
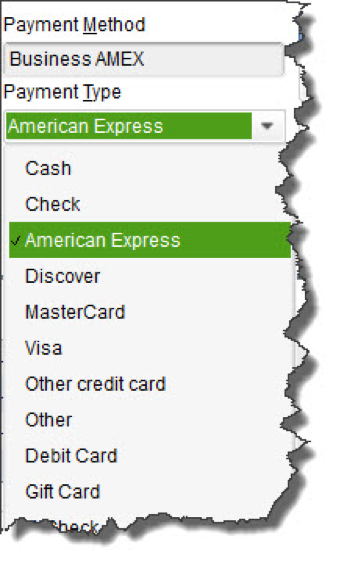
- CREDIT DEBIT (A specific card type may be shown here if you’ve indicated the customer’s preferred payment method in his or her record.)
- e-CHECK
In the last year, chatbots have exploded. A chatbot, short for chat robot, uses artificial intelligence to imitate a conversation with people. One place they have exploded is the Facebook Messenger app, which is a free instant messaging platform.
To get Facebook Messenger, you can download the app on your smartphone or go to https://www.messenger.com on your PC or Mac in any browser.
In Messenger, a chatbot looks just like a person. All you need to do to connect to a chatbot is to go to the People section and enter the name of the bot you want to connect with. Typically, there will be a Get Started button. The bot may ask you some setup questions such as your time zone, city, or topic preferences.
Bots can do many things. There are bots to deliver the news daily (Chat Newswire), bots that entertain and play games, bots that help you find recipes and restaurants, bots that improve your productivity, bots that help kids with their homework (Christopher Bot), and even a bot that connects with QuickBooks (Freelanzr).
Each bot works a little differently. In general, you will receive a welcome message, then the conversation will begin. The bot will prompt you to ask a question, enter a phrase or a word, or select from a group of horizontal button choices.
Bots are useful for your daily routine. You can get daily news, weather, reminders, and tips. If you are stuck standing in line somewhere, riding public transportation, in an Uber or taxi, or experiencing other downtime, you can have several conversations with your bots to pass the time.
If you don’t know of any bots or wonder about a bot that does a specific thing, there are lots of bot directories available. To get you started, here is one bot list: https://botlist.co/.
The cool part is you can design your own bot for your business which can be fun for customers. The Facebook Messenger platform is open, and you can find out more about how to create a bot here: https://messengerplatform.fb.com/.
There are more platforms for chatbots besides Facebook Messenger, including Twitter, Android, Slack, and Amazon Echo, to name a few that you can explore if you don’t care for Messenger or Facebook.
It’s still early for bots. The effectiveness of the bots depends on how well they are designed as well as how much time the user spends learning how to work with the bot. Try connecting with a couple of bots to see if they will be productive for you. If nothing else, your kids will love the game bots while they are standing in line with you.

Increasing your profits might sound like it’s an unattainable dream just out of your reach. But there are a finite number of ways that profits can be increased. Once you understand what they are, you’ll have clarity on how to best reach your goals.
There are two primary ways to increase profits:
- Raise revenue
- Lower expenses
That’s not particularly enlightening or instructional, is it? Let’s look at the four ways you can increase revenues and the four ways you can reduce expenses to get clearer on what actions we can take.
Four Ways to Increase Revenue
1. Raise prices
The easiest way to raise revenue is to simply raise prices. However, this is not foolproof and assumes you’ll be able to maintain the volume of sales you’ve achieved in the past.
This method is also limited by market demand, what your customers are willing to pay.
2. Add new customers
Adding new customers is what most entrepreneurs think about when raising revenue. Increasing your marketing or adding new marketing methods is typically the way to add new customers.
Another related option is to work hard to keep the customers you already have. You can also potentially contact the customers you lost and ask them to come back.
3. Introduce new products or services
For some companies, your products and services are changing every year. For others, not so much. To increase revenue, consider adding new products or services that will bring in an additional revenue stream that you didn’t have before.
Even if your products are changing every year, you can consider adding something completely different that your customer base would love. For example, a hair salon could add a nail desk, a clothing store could add handbags or shoes, a grocery store could add a coffee bar, a restaurant could add catering, a landscaper could add hardscaping, and so on.
4. Acquisition
The final way a business can increase revenue is to acquire another business in a merger or acquisition.
Four Ways to Reduce Expenses
1. Negotiate for a better deal with vendors
If you’ve been working with a vendor for a while, you may be able to re-negotiate your contract with them. This is especially common with telecom companies. Call your phone provider and ask them for the latest deal. They always favor new customers over long term customers, but they don’t want to lose customers either. Just calling them usually yields a better price than what you are paying now.
2. Change vendors
If a vendor has gotten too expensive, it might be time to look for a new vendor. Health care insurance seems to be in this category. Often, changing providers will lower your costs.
3. Cut headcount
If there is not enough work to support your employees or not enough cash flow to pay them, then it might be time for a layoff or restructuring. You might also consider outsourcing a function that you previously did in-house.
4. Cut the expense or reduce services
It might be your business no longer needs to spend money on an expense. Perhaps this expense has been automated. In this case, it’s an easy decision to cut the expense out entirely.
Those are the eight ways to increase profits. Which one makes the most sense in your business? Create a plan around these eight ideas to boost your profit in 2017, and let us know if we can help.
 New Business Direction LLC
New Business Direction LLC