New Business Directions, LLC is pleased to announce the recognition of Rhonda Rosand, CPA as an Insightful Accountant Top 100 ProAdvisor for 2016. This will be Rosand’s third consecutive year receiving the award out of tens of thousands of ProAdvisors in the country.
Leading Top 100 ProAdvisors leverage the ProAdvisor Program to better serve their clients, grow their own business, deliver great client service, and increase their knowledge and understanding of the Intuit ecosystem. This years award ceremony will take place at the Scaling New Heights 2016 conference at Atlantis Paradise Island Resort in the Bahamas.
This years award ceremony will take place at the Scaling New Heights 2016 conference at Atlantis Paradise Island Resort in the Bahamas.
Congratulations Rhonda!
Two very important skills for entrepreneurs to master are marketing and finances. Combine them by understanding the numbers behind marketing, and you have an even more powerful understanding of exactly what makes your business tick.
Key Numbers – Cost Per Client Acquisition
Do you know how much it costs your business to bring in one client? The technical term is “Cost per customer acquisition,” and it’s computed by adding the total marketing and sales costs excluding retention costs and dividing them by the total number of clients acquired during a period of time.
Cost per customer acquisition is important to know because then you can compute how long it takes before your business begins to make a profit on any one customer. In software application services with a monthly fee, the breakeven for a client can be around ten months.
It’s essential to understand this dynamic for pricing and volume planning purposes. If your services or products are priced too low so that your acquisition costs are not recouped in a reasonable period of time, it can play havoc with your cash flow as well as your profits. If you don’t have enough volume to cover overhead and acquisition costs, then your company will be in trouble in the long term.
Customer Lifetime Value
There is a simple and an academic formula for customer lifetime value. You can estimate it by multiplying the average sale of a customer by the average number of visits per year by the number of years they remain a customer. That’s the easy version.
The more difficult version of this formula takes into account retention rates and gross profit margins. The formula is: Average customer sales for life times the gross profit margin divided by the annual churn rate.
Once you know and track these numbers in your business, you’ll be better able to make smart decisions about your marketing investments and your pricing. And if we can help you, please reach out as always.
Spring denotes new growth, fresh starts, and spring cleaning. Why not apply these ideas to your sales so they can blossom along with spring flowers? Here are six ideas to put the spring into your sales.
1. Spring Cleaning Sales
Get rid of old inventory by having a spring sale that will clean out your closets and put some money in your account. Look through your items for sale and find the ones that haven’t moved like you expected. Mark them down and move them out.
2. New Items and Services from Customer Ideas
Now that you’ve gotten rid of the old stuff, you have room for new. If you’re not sure what your clients want or need, ask. Use Survey Monkey to find out what your clients can use. If you don’t have what they want, make it, buy it, or partner with someone who does. Then let everyone know, “based on popular demand” of course, that you have new items for sale just in time for spring.
What questions should you ask in your survey? Try questions like these to draw out your customers’ needs and wishes and to discover any shortcomings you might have not known about:
- What items/services are on your wish list that you’d like us to stock/provide?
- How do you currently use our services/products?
- What do you wish our items accomplished that they don’t now?
- How would you recommend we expand our selections?
- What do you wish we did better?
3. The Old “Fries with Your Burger” Upsell
Waitpersons offer desserts and appetizers, office supply staff offer cables and accessories with hardware purchases, and software vendors offer the next level package. Almost every business practices a form of upsell these days, so if you don’t, you’ve got a new opportunity right here.
Dust off your old upsell procedures and try these ideas to rejuvenate your upsells:
- Re-visit your inventory to pair complementary items for upsell potential.
- Retrain your staff for upsell language at the time of sale.
- Re-package like items to offer more bundles and groups.
4. New Prices
When is the last time you’ve raised your prices? If it’s been a while, then it’s a great opportunity to increase revenue with little additional effort.
5. Spread the Word with Spring Samples
Samples can help get your product or service into the hands of many potential buyers. Buyers can better experience your product and reduce their perceived risk.
Not all businesses can provide samples, but there is always the next best thing. Where your product is not consumable, you can sometimes provide a portion of the product, such as a carpet sample, wallpaper swatch, or floor tile. With retail clothing, pictures will have to do. With books or courses, you can provide a sample chapter or a demo video. And with services, case studies or proof of concept will suffice.
6. Offer a Customer Reward Program
Put together a program to reward your most loyal clients and to make them even more loyal to you. Some of the perks could include monthly gifts, priority service, an exclusive event, and/or discounts. The price can be structured as a membership fee, retainer, or package price. Increasing contact, benefits, and communication with these clients is always a good investment.
Try one of these six ideas to put the spring in your sales this season.
It’s not hard to see when your home needs a good cleaning but QuickBooks company file errors are harder to recognize so here are a few errors to watch for:
- Performance problems
- Inability to execute specific processes
- Occasional program crashes
- Missing data (accounts, names, dates)
- Refusal to complete transactions
- Mistakes in reports
One thing you can do on your own is to start practicing good preventive medicine to keep your QuickBooks company file healthy. Once a month or so, perhaps at the same time you reconcile your bank accounts, do a manual check of your major Lists.
Run the Account Listing report (Lists, Chart of Accounts, and Reports). Ask yourself: Are all of your bank accounts still active? Do you see accounts that you no longer use or which duplicate each other? You may be able to make them inactive or merge duplicates. Be very careful here. If there’s any doubt, leave them there. Do not try to fix the Chart of Accounts on your own. Let us help or speak with your tax preparer. Do not make accounts with balances inactive.
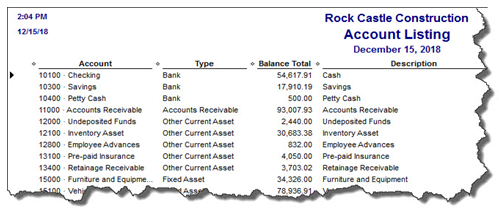
Figure 2: You might run this report periodically to see if it can be abbreviated.
A Risky Utility
The program’s documentation for this utility contains a list of warnings and preparation steps a mile long. We recommend that you do not use this tool. Same goes for Verify Data and Rebuild Data in the Utilities menu. If you lose a significant amount of company data, you can also lose your company file. It’s happened to numerous businesses.
Figure 3: Yes, QuickBooks allows you to use this tool on your own. But if you really want to preserve the integrity of your data, let us help.
The best thing you can do if you notice problems like this cropping up in QuickBooks – especially if you’re experiencing multiple ones – is to contact us. We understand the file structure of QuickBooks company data, and we have access to tools that you don’t. We can analyze your file and take steps to correct the problem(s).
Your copy of QuickBooks may be misbehaving because it’s unable to handle the depth and complexity of your company. It may be time to upgrade. If you’re using QuickBooks Pro, consider a move up to Premier. And if Premier isn’t cutting it anymore, consider QuickBooks Enterprise Solutions.
There’s cost involved, of course, but you may already be losing money by losing time because of your version’s limitations. All editions of QuickBooks look and work similarly, so your learning curve will be minimal.
We Are Here for You
We’ve suggested many times that you should contact us for help with your spring cleanup. While that may seem self-serving, remember that it takes us a lot less time and money to take preventive steps with your QuickBooks company file than to troubleshoot a broken one.
Outsmart your accountant and other financial friends with these accounting-related definitions:
Fiscal Year
Most companies report their results on a calendar year, from January 1 through December 31. Some companies use a different year for reporting, and that’s called a fiscal year. For example, Intuit’s fiscal year runs from August 1 to July 31. A nonprofit commonly runs from July 1 to June 30.
The word fiscal alone refers to government or public revenues and expenditures. A fiscal year can also be considered the period where companies report their financial results to the public.
Budget
Most companies sit down once a year and plan what they intend to spend. This set of numbers is a budget. It is prepared in income statement format which includes planned revenue and expenses. It can be done for a year, monthly or both.
A common report that compares budget to actual figures is the Income Statement Comparison to Budget which includes columns for month and year-to-date actual, budget, and variance (the difference).
Forecast
While a budget is a longer term plan, a forecast is an attempt to predict the short-term future. Forecasts can be made for cash flow, predicting your bank account balance, or can be focused on potential profit for a period. A forecast is created by enumerating current and expected short-term cash commitments.
General Ledger
A general ledger is a fancy word for your accounting books. It’s also a very specific report that lists each account within the chart of accounts, beginning balances, the activity of each account for a particular period of time, and ending balances. It includes both balance sheet accounts, such as cash, accounts receivable, and accounts payable, and income statement accounts, such as revenue and expenses.
Fixed Asset
A fixed asset is a special type of asset that includes items such as land, vehicles, furniture, buildings, office equipment, plants, and machinery. Fixed assets cannot easily be converted into cash (cash equivalents are termed current assets) and they must last longer than one year. They are physical or tangible (as opposed to intangibles such as patents and trademarks).
Depreciation
Most fixed assets except land depreciate in value over time. For example, when you drive a new car out of the lot, no one will give you what you just paid for it. This reduction in value over time is recognized on accounting books by recording depreciation. Since assets need to be recognized at market value, depreciation is an estimate of this adjustment. Depreciation becomes an expense and reduces the value of the fixed asset. Unlike most other transactions, cash is not affected when recording depreciation.
Accrual
There are two ways to keep books when it comes to the timing of how items are recorded: the cash method and the accrual method. Let’s invoke Popeye the Sailor Man’s friend Wimpy who always says, “I’ll gladly pay you Tuesday for a hamburger today.” Let’s say today is the Friday before this famous Tuesday.
If you are using the cash basis method, you would record the entire transaction on Tuesday, when you get the cold hard cash. If you are using the accrual basis, you would have two entries: one on Friday to record the sale to accounts receivable and one on Tuesday to zero out the receivable and increase cash. It’s the same net, effect; the only difference is in the timing.
Most small businesses that extend credit keep their books on an accrual basis so they can keep track of everything. Most taxes are paid on cash-basis books, requiring adjusting entries at year end that reverse at the beginning of the year.
Balance Sheet
A balance sheet is a very common report of all of the business’s account balances as of a specific date, such as December 31. These accounts include cash, receivables, fixed assets, liabilities, equity and others.
Journal Entry
A journal entry is usually an adjustment that is made to the accounting books. The result is that some accounts increase and others decrease. In theory, every transaction made to a company’s books is a journal entry. When you write a check and it’s cashed, cash goes down and an expense is increased. When you receive a payment, cash goes up and revenue goes up. Each of these transactions is a journal entry.
Do you feel a bit smarter? I’m not sure how exciting this is for cocktail table talk, but hopefully you feel smarter when it comes you’re your business’s accounting function.
 New Business Direction LLC
New Business Direction LLC